Dictionary is an
abstract class that has Keys and Values.
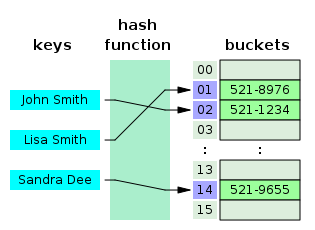
The HashTable class extends the Dictionary abstract class. HashTable class implements a hash
table. In the HashTable , keys are segmented
into buckets based on their hash code. Thus, a key must
expose the methods hashCode() (for bucket segment) and equals
(to compare the two keys in the same bucket). For example, String has both
method hashCode and equals, so it can be used as
key type in a HashTable.
Let us declare a HashTable that maps a key of
type String to a value of type String
Dictionary abstract class
has Keys and Values
Dictionary
----------------> has Keys and Values
key
----------------> has
hashCode() and equals()
Bucket
----------------> is
Hash table here
String is a key because it has hashCode() and equals()
methods. A keys goes inside a dictionary, so it does inside a hashtable which
extends a dictionary.Let us create a hashtable instance “Contacts”.
Hashtable<String,
String> contacts = new Hashtable<String, String>();
Now this instance “Contacts is instance of Class “Hashtable” and
Hatshtable extends “dictionary class. So that means the Keys and Values that
dictionary class has have also been inherited by “Contacts” object(instance of
a class). So we will condider a person’s name as “Key” here & His email
address as “value” .
So what all operations can we perform with this Key-Value pair?
Let’s see :
We can put person’s name as “Key” &
email address as “value” in the “Contacts” hashtable object
put(Key, Value);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public int addContact(String name, String emailAddress) {
put(Key, Value);
if (hasEmailAddress(emailAddress) || hasName(name)) {
return 0;
} else {
contacts.put(name, emailAddress);
return 1;
}
}
|
We can get person’s name & email
address from “Contacts” hashtable object
get(Key);
1
2
3
|
public String findEmailAddress(String name) {
return contacts.get(name);
}
|
We can remove
a person’s name & email address from “Contacts” hashtable object
remove();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public int deleteContact(String name) {
if (hasName(name)) {
contacts.remove(name);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
|
Check
if a Key (name) exists in the contact book, we use containsKey method
containsKey ()
1
2
3
|
public boolean hasName(String name) {
return contacts.containsKey(name);
}
|
Check
if a KeyValue(emailAddress) exists in the contact hashtable , we use containsValue method
containsValue()
2
3
|
1. public boolean
hasName(String name) {
2. return contacts.containsValue (emailAddress);
}
|
To get
a complete Set of Keys (names) from the contact hashtable , we use keySet() method
keySet()
1
2
3
4
5
|
// Get the name Set
for (String name : contacts.keySet()) {
String emailAddress = contacts.get(name);
System.out.printf("%-10s|%-20s\n", name,
emailAddress);
}
|
Points to remember :
·
Dictionary is
an abstract class that has Keys and Values
·
The HashTable class extends the Dictionary abstract class
Recommended Reading:

Comments